- Home
- Elbow Pain Diagnosis
Elbow Pain Diagram
Written By: Chloe Wilson BSc (Hons) Physiotherapy
Reviewed By: SPE Medical Review Board
An elbow pain diagram can be a really useful tool for helping you work out what the underlying cause of elbow and forearm pain is.
There are lots of different structures in and around the elbow from ligaments to tendon and bones to nerves.
Irritation, injury, compression or damage to any of these structures can cause elbow pain which may be quite localised or extend right down the forearm and into the hand. Diagnosing elbow pain can be tricky, but thinking about where your pain is and the associated symptoms can help you on your way to an accurate elbow pain differential diagnosis.
Elbow Pain Diagnosis Charts
Here we will look at three different ways to work out what is causing you elbow pain incorporating elbow pain diagrams and symptoms checkers to help:
- Inner Elbow Pain Diagram: for anterior and medial elbow pain differential diagnosis
- Outer Elbow Pain Diagram: for posterior and lateral elbow pain differential diagnosis
- Elbow Pain Symptom Checker: e.g. popping, tingling and swelling and what they indicate
If your pain is slightly further down the arm, check out the Forearm Pain or Wrist Pain Chart sections.
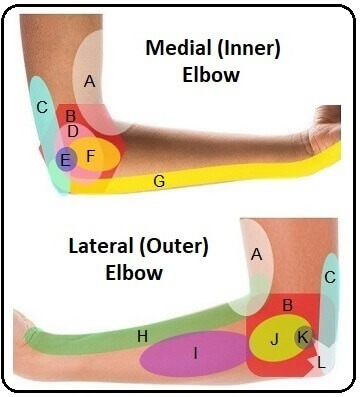
Inner Elbow Pain Diagram
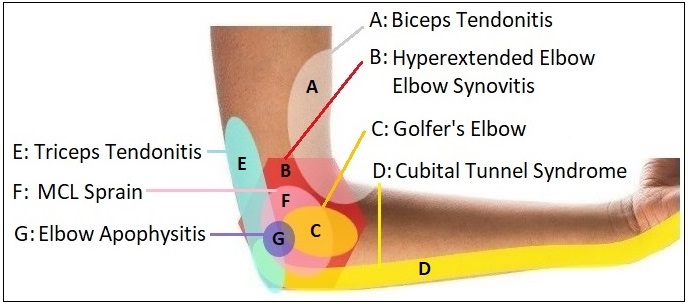
Inner elbow pain, aka medial elbow pain, is a common problem, often caused by overuse or a one-off injury. The pain may be confined to a specific point around the inner elbow, or may extend to the front of the elbow or down the forearm towards the little finger.
This inner elbow pain diagram focuses on elbow problems that cause pain at the front and inner side of the elbow and forearm.
A. Biceps Tendonitis
Biceps tendonitis is caused by inflammation and wear and tear of the distal biceps tendon at the elbow, usually from overuse. Typical symptoms include a deep, throbbing ache at the front of the elbow which often extends out to the sides. There may be a snapping sound with arm movements and pain gets worse with activity. LEARN MORE >
B. Hyperextended Elbow
A hyperextended elbow is when the elbow bends back too far, usually during sports or from a fall. It can damage multiple structures in and around the elbow resulting in intense pain, stiffness, weakness and swelling. LEARN MORE >
C. Golfer’s Elbow
Golfer’s elbow, aka medial epicondylitis, is the most common cause of inner elbow pain. It is caused by damage to the forearm tendons on the inner elbow usually from overuse. Typical symptoms include pain and tenderness over the inner elbow that gets worse with activity, and weakness in the wrist and hand. Symptoms usually build up slowly over time. LEARN MORE >
D. Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
Cubital tunnel syndrome is caused by pinching or irritation of the ulna nerve. This may be from direct pressure, repetitive elbow bending, fluid build-up or a direct blow. Cubital tunnel syndrome causes inner elbow pain that radiates into the hand causing tingling and numbness in the ring and little finger - it feels very similar to when you hit your “funny bone”. LEARN MORE >
E. Triceps Tendonitis
Triceps tendonitis develops when there is inflammation of the triceps tendon at the back of the elbow, typically from overuse. It causes an aching pain and tenderness at the back of the elbow that gets worse with activity, weakness, stiffness and sometimes swelling. LEARN MORE >
F. MCL Sprain
An MCL sprain is where there is damage to the medial collateral ligament that connects the elbow bones together. Tearing and inflammation may develop from repetitive wear and tear or a sudden over-stretching of the ligament. MCL sprains cause inner elbow pain and instability and can affect throwing speed and accuracy. LEARN MORE >
G. Elbow Apophysitis
Also known as Little League Elbow, apophysitis is a common cause of inner elbow pain in children. Sports that require repetitive throwing can irritate the growth plate causing inflammation and damage to the growth plate resulting in pain and stiffness in the elbow. LEARN MORE >
If you want more help working out what is causing your medial elbow pain, visit the inner elbow pain diagnosis section.
Lateral Elbow Pain Diagram
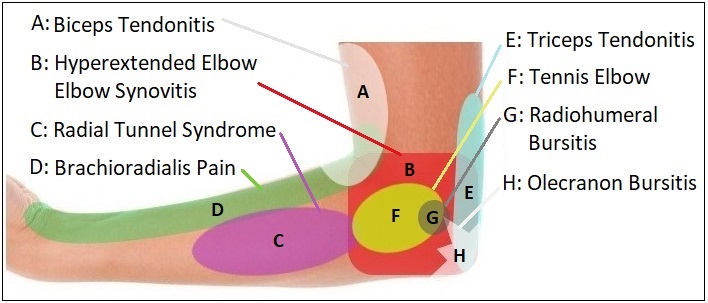
This lateral elbow pain diagnosis chart focuses mainly on the causes of pain on the outer side of the elbow, but also incorporates some conditions that cause pain at the front or back of the elbow too. If you pain is concentrated right at the back of the elbow, check out the pain behind the elbow section.
A. Biceps Tendonitis
Biceps tendonitis, as mention above, causes pain at the front of the elbow that can extend around both sides. Typically caused by overuse from heavy lifting or sports, inflammation and degeneration of the tendon causes pain. LEARN MORE >
B. Hyperextended Elbow
A hyperextended elbow can cause pain around the entire elbow joint and is caused by the elbow being forced back too far. This can lead to damage to the soft tissues and bone in and around the elbow joint. An elbow hyperextension injury is usually very painful and can result in swelling and restricted motion at the elbow. LEARN MORE >
Elbow Synovitis
Elbow synovitis develops when there is inflammation of the synovial membrane that lines the elbow joint. It can develop due to an injury, infection or underlying medical condition. Synovitis typically causes elbow pain, swelling, stiffness and warmth. LEARN MORE >
C. Radial Tunnel Syndrome
Radial tunnel syndrome causes outer forearm pain and weakness, usually around 3cm below the elbow joint. Repetitive pressure on the radial nerve from repetitive gripping and twisting movements, e.g. using a screwdriver, or a direct blow leads to compression or inflammation of the nerve. It causes a nagging or burning pain that gets worse with any gripping activities and can lead to decreased grip strength. LEARN MORE >
D. Brachioradialis Pain
Brachioradialis pain causes tightness and pain in the outer forearm, usually from overuse. There is typically a background ache at rest with a sharp shooting pain with activity. Brachioradioalis pain may extend into the back of the hand, thumb and index finger. Grip strength may be affected but there isn’t usually any tingling or numbness. LEARN MORE >
E. Triceps Tendonitis
Triceps tendonitis causes back of elbow pain that may spread across the joint. Irritation and inflammation of the triceps tendon where it attaches to the back of the elbow is typically caused by overuse and usually responds well to home treatment. LEARN MORE >
F. Tennis Elbow
Tennis elbow, aka lateral epicondylitis, is the most common cause of outer elbow pain. Overuse of the wrist and hand extensor muscles causes irritation and inflammation in the common extensor tendon. Tennis elbow is just as likely to affect office workers as tennis players so don’t be fooled by the name. Most cases of tennis elbow will get better by themselves within a couple of years, but the recovery time can be significantly reduced with appropriate treatment. LEARN MORE >
G. Radiohumeral Bursitis
Radiohumeral bursitis causes localised outer elbow pain and swelling. Irritation and inflammation of the bursa may develop due to repetitive forearm movements, an infection or a direct injury to the joint. Bursa are small, fluid-filled sacs that allow smooth, friction-free movement between bones and soft tissues. LEARN MORE >
H. Olecranon Bursitis
Olecranon bursitis is the most common cause of pain and swelling at the back of the elbow. Damage to the bursa from an injury or repetitive pressure/friction causes the bursa to swell forming a soft pocket of swelling, similar to a squash ball, at the back of the elbow. It can make it very uncomfortable to lean through your elbow. Treatment aims to reduce the swelling and can usually be done at home. LEARN MORE >
If you are still not sure what is causing your lateral elbow pain, visit the outer elbow pain diagnosis section, or if the pain is more at the back of your elbow, visit the posterior elbow pain section.
Wrist Pain
Sometimes pain is more around the wrist region with inner wrist pain (pinky side), outer wrist pain (thumb side) or central wrist pain. Some of the most common causes of wrist pain are:
- Wrist Fractures: a break in one of the wrist bones, common after a fall
- Wrist Tendonitis: inflammation of the wrist tendons, typically a repetitive strain injury
- Ulnar Styloid Fractures: a type of wrist fracture where the tip of the inner forearm bone breaks
- Smith's Fracture: a type of wrist fracture usually caused by falling onto a bent wrist
- Barton's Fracture: a wrist fracture that involves the joint surface
- Colles Fracture: most common type of wrist fracture
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: compression of the median nerve at the wrist
Find out more in the Wrist Pain Diagnosis Chart section and get help working out what is wrong
Elbow Pain Symptom Checker
There are lots of things that can cause pain in and around the elbow and elbow pain differential diagnosis can be confusing. But by thinking about the location of the pain and the associated symptoms, it becomes much easier to work out what might be wrong.
This elbow pain symptoms checker can help you work out what is going on:
Localised Inner Elbow Pain: Pain that is confined to the inner elbow area only is usually caused by medial epicondylitis, elbow apophysitis or an MCL sprain
Inner Elbow Pain That Extends Towards The Hand: if the pain extends towards the hand and into the thumb and ring fingers it usually indicates a nerve issue, most typically from cubital tunnel syndrome or an ulnar nerve contusion
General, Diffuse Elbow Pain: pain that is felt throughout a large part of the elbow is typically caused by a hyperextended elbow or elbow synovitis
Front Elbow Pain: pain right at the front of the elbow is typically caused by biceps tendonitis
Back Of Elbow Pain: pain behind the elbow is typically caused by triceps tendonitis. It there is a pocket of swelling behind the elbow, it is usually from olecranon bursitis
Localised Outer Elbow Pain: pain that is confined to the outer elbow joint region is likely from lateral epicondylitis or radiohumeral bursitis
Lateral Elbow Pain That Extends Towards The Hand/Thumb: outer elbow pain that extends down the forearm may be radial tunnel syndrome or brachioradialis pain. If there is tingling and numbness associated with it in the hand, it is likely from arm nerve pain
Elbow Popping: if there is a popping or snapping noise, either at the time of injury or whenever you move the elbow, it could be from biceps tendonitis, hyperextended elbow or triceps tendonitis
Elbow Pain With Hand Tingling Or Numbness: tingling or numbness indicates there is a problem in one of the nerves. Altered sensation in the thumb, index and middle finger indicates a radial nerve problem whereas altered sensation in the ring and little finger indicate a ulna nerve compression from cubital tunnel syndrome, ulna nerve contusion or a problem in the neck. Generalised tingling through the arm can also indicate restless arm syndrome
Swollen Elbow: swelling at the back of the elbow usually indicates olecranon bursitis. Generalised swelling in the elbow indicates a problem within the joint such as a hyperextended elbow injury or synovitis. A more defined lump on elbow may be from bursitis, tendonitis, bone injury or a cyst.
Elbow Pain Diagnosis Summary
There are lots of different elbow pain causes, but they all present slightly differently as shown on each elbow pain diagram here.
If you’re still not sure what is wrong or want more help making an elbow pain differential diagnosis, check out the following articles:
If your also have pain above your elbow, chances are it is from a problem higher up the arm in the shoulder or neck, in which case check out the shoulder pain diagnosis charts for help working out what is wrong.
By using the elbow pain diagrams here you will be on your way to making an elbow pain differential diagnosis, but this is no substitute for medical advice and any new incidence of elbow pain should be checked out by your doctor.
And remember, early elbow pain diagnosis is really important as the sooner you start treatment, the quicker your recovery time and the faster you will get back to doing the things you love.
Hopefully, these elbow pain diagram diagnosis charts have given you a clearer idea of what your problem might be. You can find out loads more about the causes, symptoms, treatment options and recovery process for each by using the links above to take you to the relevant articles.
Related Articles
Medical & Scientific References
- British Journal Of General Practice - Elbow pain: a guide to assessment and management in primary care. Javed M, Mustafa S, Boyle S, Scott F. November 2015
- NHS UK: Elbow & Arm Pain. February 2021
Page Last Updated: February 28, 2025
Next Review Due: February 28, 2027