- Home
- Elbow Pain Diagnosis
- Inner Elbow Pain
Inner Elbow Pain
Written By: Chloe Wilson BSc (Hons) Physiotherapy
Reviewed By: SPE Medical Review Board

Inner elbow pain is a common problem that can affect people at any age.
We are constantly using our arms, whether we’re lifting or carrying things, twisting to open things or picking things up, leaning through our elbows for support or playing sports.
This can place excess pressure through the elbow resulting in inner elbow pain, particularly repetitive actions like throwing, lifting and typing.
Inner elbow pain usually originates from the soft tissues around the elbow and may extend down the forearm to the wrist. In some cases, it is accompanied by tingling, numbness and weakness in the hand. If your pain is more around the back of your elbow, check out the posterior elbow pain article.
Causes Of Inner Elbow Pain
There are three common causes of inner elbow pain, Golfer’s Elbow aka medial epicondylitis, Biceps Tendonitis and Cubital Tunnel Syndrome aka ulnar nerve entrapment. We'll start by looking at these and then go on to look at some of the rarer causes of medial elbow pain.
1. Golfer’s Elbow
The most common cause of inner elbow pain is Golfer’s Elbow, aka medial epicondylitis.
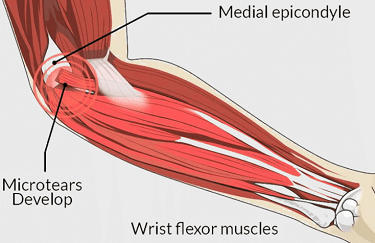
Golfer’s elbow develops when there is irritation and inflammation of the common flexor tendon that attaches onto the medial epicondyle, a bony lump on the inner side of the humerus (upper arm bone).
Medical epicondylitis is usually caused by repetitive overuse of the forearm muscles that help to you grip, twist your arm and bend your hand and fingers. Common activities that cause inner elbow pain from medial epicondylitis include manual labour, racket sports, throwing sports and heavy lifting.
Golfer’s elbow typically causes localised tenderness and inner elbow pain which may extend down the forearm to the wrist. There doesn’t tend to be any pain in the hand but there may be weakness causing difficulty with gripping and twisting activities e.g. opening jars.
Treatment for golfer’s elbow usually involves a combination of rest, activity modification, exercises and injections and some people find it helpful to wear a specially designed elbow brace.
You can find out loads more about the symptoms, causes, diagnosis and treatment options in the golfer’s elbow section.
2. Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
Another possible cause of inner elbow pain is cubital tunnel syndrome aka ulnar nerve entrapment or ulnar neuritis.
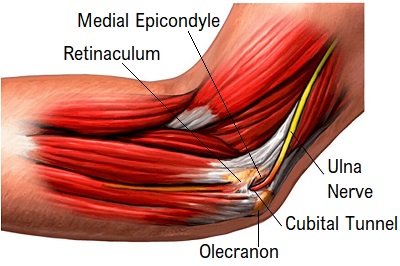
Cubital tunnel syndrome develops when there is compression and irritation of the ulna nerve as it travels round the inner side of the elbow.
Frequent or prolonged pressure on the nerve e.g. from bending or leaning on the elbow for long periods, can squash or irritate the nerve resulting in ulnar nerve entrapment.
Common features of cubital tunnel syndrome are inner elbow pain accompanied by tingling and/or numbness in the ring and little fingers. There may also be some weakness in the hand affecting grip strength and dexterity.
In most cases, medial elbow pain from cubital tunnel will settle with a combination of rest, medications, injections, exercises and wearing a cubital tunnel syndrome brace, but some people require surgery to reduce the pressure on the nerve.
You can find out loads more about the causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment in the Cubital Tunnel Syndrome section.
3. Biceps Tendonitis
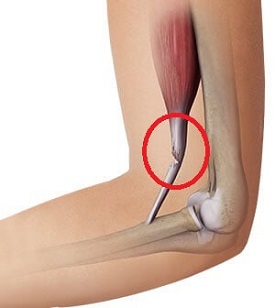
Distal biceps tendonitis is an overuse injury that causes inner elbow pain where the muscles inserts at the top of the forearm.
Insertional biceps tendonitis is caused by irritation, inflammation or degeneration of the tendon from overloading. This may be from heavy lifting, repetitive activities e.g. racket sports and throwing sports, sudden increases in activity levels and aging.
Distal biceps tendonitis typically causes a deep, throbbing ache at the front and inner side of the elbow that gets worse with activities using the biceps muscle e.g. lifting, pulling and throwing. Inner elbow pain from biceps tendonitis is often worse at night and the area is often tender to touch.
A simple diagnostic test for biceps tendonitis is to resist elbow flexion (with the palm facing up) – if this causes pain at the elbow, you likely have biceps tendonitis.
Treatment for inner elbow pain from biceps tendonitis usually involves a combination of rest, ice, medication, steroid injections, physical therapy, exercises and friction massage. In rare cases, surgery may be necessary.
You can find out more about the common causes, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment options in the biceps tendonitis section.
Other Causes Of Medial Elbow Pain
There are some other possible causes of inner elbow pain that are less common:
1. Elbow Apophysitis
Elbow apophysitis is the most cause of inner elbow pain in children, typically aged 9-14, also known as “little league elbow”.
While the bones are still growing, the growth plate can become irritated and inflamed if placed under too much stress.
Repetitive throwing, particularly if there is muscle imbalance or poor technique, irritates the growth plate at the elbow and in severe cases may cause it to break away from the arm bone.
Common symptoms of elbow apophysitis include inner elbow pain when throwing a ball which may affect speed and accuracy, and difficulty fully straightening the elbow.
The best way to treat little league elbow is complete rest from aggravating activities, typically throwing, so that the growth plate can heal properly. Ice, exercises and physical therapy can also help reduce inner elbow pain. In most cases, medial elbow pain from apophysitis will settle within a few weeks with correct treatment.
2. Ulnar Nerve Contusion
An ulnar nerve contusion is essentially a bruise of the ulna nerve. It is typically caused by a direct blow to the nerve at the elbow, usually from a fall, banging your elbow against something or a sporting tackle.
At the time of injury, it will feel like you hit your “funny bone” with intense pain at the inner elbow and a shooting pain into the hand. There may also be tingling in the fourth and fifth fingers. In most cases, the symptoms will settle within a few minutes, but if they persist for more than a few hours, it implies a more severe contusion and you should seek medical advice.
The symptoms of an ulnar nerve contusion are similar to those with cubital tunnel syndrome, but they tend to be more sudden and short lived as the nerve is usually only temporarily compressed.
3. Elbow MCL Sprain
Another possible cause of inner elbow pain is an injury to the medial collateral ligament aka ulnar collateral ligament or MCL.
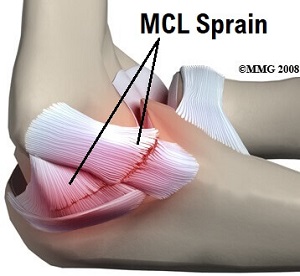
The MCL runs down the inner side of the elbow and is actually made up of three ligaments that attach to and stabilise the upper arm bone (humerus) to one of the forearm bones (ulna).
The MCL resists valgus forces through the elbow, where the forearm is pushed outwards in comparison to the upper arm when in supination (palm up).
Elbow MCL sprains are usually overuse injuries caused by repetitive wear and tear on the ligament from repetitive throwing e.g. javelin or baseball pitching. In the late cocking and early acceleration phases of throwing, the elbow is placed in a valgus stress position which increases the tension through the MCL.
Frequent repetition of this movement can cause micro-tearing in the ligament resulting in a gradual onset of inner elbow pain, instability and reduced speed and accuracy with throwing.
MCL sprains can occasionally be caused by acute trauma, typically involving elbow dislocations where the humerus is pushed inwards while the forearm is pulled outwards e.g. sporting tackle or awkward fall. With acute injuries there will be a sudden onset of intense inner elbow pain and rapid swelling, and bruising will appear within a few hours.
Treatment for elbow MCL sprains usually involves a combination of:
- RICE: rest, ice, compression & elevation
- Physical Therapy: which may include friction massage, ultrasound and a rehab program of strengthening and stretching exercises
- Taping: or bracing to support the injured ligament and improve stability
- Surgery: in severe cases if the ligament has completely ruptured
4. Elbow Avulsion Fracture
An elbow avulsion fracture occurs when excessive tension through one of the ligament or tendons causes it to tear, pulling off a small fragment of the bone it was attached to.
The mechanism of injury is very similar to that with an MCL sprain and often the only way to tell the difference is with an X-ray or MRI scan. Treatment for the two conditions will be similar but more severe elbow avulsion fractures may require wearing a brace or cast for 4-8 weeks or surgery to reattach the broken bone.
5. Osteochondritis Elbow
Osteochondritis dissecans of the elbow is a condition caused by restricted blood flow to the elbow joint. This starves the bone of vital nutrients and over time, causes the bone and cartilage to degenerate and in some cases break off. Osteochondritis elbow typically affected teenagers who repetitively overload the joint e.g. baseball, volleyball and gymnastics.
Elbow pain from osteochondritis dissecans typically gets worse with activity and improves with rest. If fragments of the bone or cartilage break off, they can get stuck in the joint and inhibit elbow movement, particularly end-range extension.
The exact cause of osteochondritis dissecans is unknown but there is thought to be a genetic link. Osteochondritis typically causes more lateral elbow pain but should certainly be considered in adolescents with inner elbow pain.
Inner Elbow Pain By Symptoms
There are many possible causes of inner elbow pain and each will present with slightly different symptoms:
Inner Elbow Pain From Lifting Weights: If you get medial elbow pain while lifting weights or shortly afterwards, it is most likely from distal biceps tendonitis
Inner Elbow Pain With Hand Weakness: If your medial elbow pain is accompanied by some weakness in your hand, particularly when gripping things, it may indicate cubital tunnel syndrome, golfers elbow or nerve pain
Inner Elbow Pain That Extends Down The Forearm: if your medial elbow pain extends down into your forearm to the wrist if can indicate golfers elbow. If there is a shooting pain down the forearm into the hand, it is likely cubital tunnel syndrome or an ulnar nerve contusion
Inner Elbow Pain In Teenagers: the most common causes of medial elbow pain in teenagers are osteochondritis dissecans and avulsion fractures
Inner Elbow Pain In Children: medial elbow pain in children under the age of 14 is usually cause by elbow apophysitis
Medial Elbow Pain With Altered Sensation: if you inner elbow pain is accompanied by tingling or numbness in the hand it indicates a nerve problem and is typically caused by cubital tunnel syndrome or ulnar nerve contusion
Inner Elbow Pain Affecting Throwing Activities: if you notice a decrease in your throwing speed or accuracy, it usually indicates an MCL sprain or elbow apophysitis
Inner Elbow Pain With Swelling: if you notice and elbow lump or swelling on the inner side of your elbow it may indicate golfers elbow or an MCL avulsion fracture. If the swelling is more at the front of your elbow, you may have biceps tendonitis or a biceps avulsion fracture
Inner Elbow Pain After A Workout: pain after a workout implies you have overloaded the soft tissues and may be a sign of an MCL sprain, golfers elbow, biceps tendonitis or osteochondritis
Inner Elbow Pain With Racket Sports: if you mainly notice your pain when playing racket sports e.g. tennis or squash, you probably have golfers elbow
Inner Elbow Pain With Throwing Sports: Of you pain is worse when doing throwing activities, it can indicate an MCL strain (adults), elbow apophysitis (children), avulsion fracture (teens) or medial epicondylitis
Medial Elbow Pain When Climbing: inner elbow pain in climbers is usually due to medial epicondylitis
Medial Elbow Pain That Gets Worse With Gripping or Twisting: If your inner elbow pain gets worse when you grip things, particularly combined with rotation e.g. opening jars or using a screwdriver, it is most likely due to golfers elbow or biceps tendonitis
Inner Elbow Pain Treatment
The best course of treatment for inner elbow pain will depend on the underlying cause. In most cases, the best place to start is to rest from any aggravating activities to allow the affected tissues to heal.
This may be combined with medication, steroid injections, physical therapy and rehab exercises to improve the strength, flexibility and endurance of the elbow.
You can find out more about how to treat the most common causes of inner elbow pain in the biceps tendonitis, golfers elbow and cubital tunnel syndrome sections.
Alternatively, if the pain is more on the outer side of your elbow, visit the lateral elbow pain section or if you want more help working out what is wrong, have a look at our elbow pain diagnosis charts. If the pain extends further down your arm, check out the forearm pain diagnosis section.
Inner Elbow Pain Summary
Inner elbow pain is a common problem that can affect anyone.
The most common cause is medial epicondylitis (golfer's elbow) where there is inflammation and tearing of the common flexor tendon.
If the pain is more towards the middle of your elbow, it is likely to be biceps tendonitis
If your inner elbow pain is associated with tingling or numbness then you may have cubital tunnel syndrome or nerve pain.
Treatment for medial elbow pain will depend on the underlying cause but may involve a combination of rest, ice, exercises, medications and splinting.
You may also be interested in the following articles:
- Outer Elbow Pain
- Pain Behind The Elbow
- Forearm Pain
- Forearm Tendonitis
- Upper Arm Pain
- Arm Nerve Pain
- Arm Stretches
- Elbow Lumps
Page Last Updated: 03/13/2024
Next Review Due: 03/13/2026
Related Articles
Medical & Scientific References
- National Library Of Medicine - Efort Open Reviews: Medial Elbow Pain. By Barco R, Antuña SA. August 2017
- Columbia University Irving Medical Centre: Medial Epicondyle Apophysitis / Little League Elbow (Pediatric)