- Home
- Wrist Pain Diagnosis
- Back Of Hand Pain
Pain In Back Of Hand:
Causes, Symptoms & Treatment
Written By: Chloe Wilson BSc (Hons) Physiotherapy
Reviewed By: SPE Medical Review Board

Pain in the back of your hand can be frustrating, especially when it affects simple day-to-day tasks like typing, gripping, or lifting.
The back of the hand is packed with small joints, tendons, nerves and ligaments, so even a minor irritation can cause sharp pain, aching, stiffness, or weakness.
In this guide, I’ll walk you through the most common causes of back of hand pain, how to work out what’s going on, what symptoms to look out for, and the best treatment options — based on what I use every day as a physio so you can get back to normal as quickly as possible.
Quick Glance: Pain in Back of Hand
Most Common Causes: extensor tendonitis, joint irritation, ligament sprains, nerve compression, ganglion cysts, overuse strain
Common Symptoms: aching, stiffness, sharp pain with gripping, swelling, tenderness, burning or tingling
Best Treatments: rest, splints, ice/heat, physical therapy, ergonomic changes, gradual strengthening
When To See A Doctor: swelling after injury, numbness, visible bumps, persistent pain > 3 weeks
What Is Pain in the Back of the Hand?
Pain in the back of the hand (also called dorsal hand pain or posterior hand pain) refers to discomfort felt on the top side of the hand between the wrist and the knuckles.
Common symptoms of posterior hand pain include:
- A dull ache or throbbing pain on back of hand
- Sharp pain back of hand when gripping, typing or twisting
- Burning, tingling or throbbing after repetitive activities
- Tenderness when pressing over tendons or joints
- Stiffness, especially first thing in the morning
- Swelling or visible lumps
- Reduced grip strength
Main
Causes of Back Of Hand Pain
Pain on the back of the hand can come from many sources, including irritated tendons, inflamed joints, compressed nerves, or small injuries. Knowing the main causes of back of hand pain helps you target the right treatment so let’s get started.
1. Tendon Problems
The back of the hand is packed with extensor tendons, long cords that straighten your fingers and wrist.
When overloaded or irritated, these tendons become inflamed or irritated, leading to localised aching, sharp pain on movement and tenderness along the tendon paths.
Tendon problems are one of the most common reasons people develop pain in the back of the hand, especially if they spend long hours typing, gripping tools, lifting weights, or doing repetitive wrist movements.
Common tendon problems that cause back of hand pain are:
- Extensor Tendonitis: inflammation from repetitive overuse (typing, gripping, lifting)
- Intersection Syndrome: friction where tendons cross near the wrist
- De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis: affects the thumb tendons but pain can radiate onto the dorsum of the hand
- Tendon Strain: sudden overloading during sport, weights or manual work
Typical symptoms:
Aching, burning, pain with finger/wrist extension, tenderness along tendon lines.
2. Joint Problems
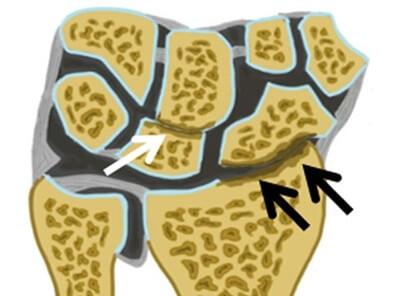
The back of the hand is also home to several important joints, including the wrist joints, knuckles, and carpometacarpal joints.
These joints can develop pain from everyday wear-and-tear, previous injuries, or inflammatory conditions.
When joint surfaces become worn or inflamed, they produce stiffness, swelling, deep aching and back of hand pain during gripping or fist making.
Common joint problems that cause posterior hand pain are:
- Carpometacarpal (CMC) Irritation: pain at the base of the hand near the wrist
- Metacarpophalangeal (MCP) Arthritis: knuckle pain that spreads across the back of the hand
- Wrist Arthritis: including post-traumatic arthritis
- Early Rheumatoid Arthritis: often starts in the knuckles
Typical Symptoms:
Stiffness (especially first thing in the morning or after resting), swelling, reduced grip strength, pain with gripping or fist-making.
3. Bone Injuries
The bones in the hand are small but highly active, absorbing significant force every time you grip, push, punch, or catch yourself during a fall. Even minor fractures or bone bruises can cause significant pain on the back of the hand, especially when pressing on the area or trying to grip objects.
Bone injuries often go unnoticed at first, particularly stress fractures or small carpal fractures, but become progressively more painful with use.
Common bone-related causes of pain on the back of the hand are:
- Metacarpal Fractures: especially 2nd, 3rd & 5th metacarpals with punching or impact
- Carpal Bone Fractures: most typically scaphoid fracture or triquetrum fractures
- Stress Fractures: from repetitive lifting or sports
- Bone Bruising: often overlooked but very painful
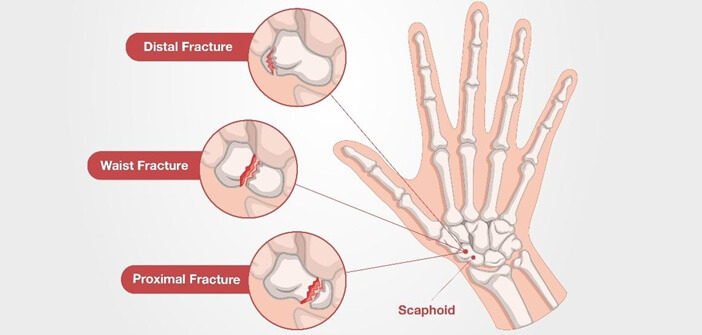
Typical symptoms of bone injuries:
Localised tenderness, swelling, sharp pain with pressure or gripping, reduced range of motion.
4. Ganglion Cysts
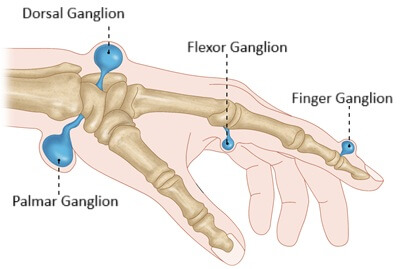
Ganglion cysts are among the most common visible causes of pain on the back of the hand, forming a soft or firm lump.
These fluid-filled sacs develop when joint or tendon sheath lining bulges outward, often due to irritation or repetitive strain. Ganglion cysts often change size and can cause back of hand pain, particularly when you bend the wrist.
Typical symptoms:
Visible bump, aching, sharp pain when pushing up from a chair, weakness.
5. Ligament Sprains or Instability
Ligaments on the back of the hand help stabilise the small joints and keep the wrist steady during movement. When these ligaments are overstretched, torn, or irritated, they can cause sharp or persistent dorsal hand pain.
Sprains commonly occur after falls, sudden twists, or weight-bearing activities - like pushing yourself up from the ground. Instability in key wrist ligaments can create deeper, hard-to-localise pain and clicking.
Common causes of back of hand pain from ligament injuries are:
- Wrist Ligament Sprains: from falls or injuries
- Dorsal Wrist Impingement: pinching of soft tissue during wrist extension
- Scapholunate Ligament Injury: causes deep wrist pain that spreads onto the back of the hand
Typical Symptoms:
Sharp pain with lifting or weight-bearing, clicking/popping, weakness.
6. Nerve Irritation or Compression
Nerves that supply the back of the hand can easily become irritated by pressure, tight straps, repetitive wrist motion, or even neck problems.
When compressed, these nerves can create burning, tingling, or electric-shock pain across the back of the hand - often in very specific patterns depending on which branch is affected.
The main nerve issues that cause pain on back of hand are:
- Radial Nerve Irritation: especially at the forearm or wrist
- Wartenberg’s Syndrome: superficial radial nerve compression
- Cervical (Neck) Nerve Irritation: can refer pain into the hand
Typical symptoms:
Burning, tingling, electric-shock pain and altered sensation e.g. numbness.
7. Overuse & Repetitive Strain
The back of the hand is especially vulnerable to repetitive strain because the extensor tendons and small joints are used constantly throughout the day. Frequent typing, gripping, lifting, DIY activities, or long periods of handheld tool use can overload the tissues without causing a single obvious injury.
Overuse problems often develop gradually and may feel worse at the end of the day or after heavy activity.
Causes of dorsal hand pain from repetitive overuse include:
- Typing or computer work
- Lifting weights
- Repetitive gripping or pinching
- Manual work (DIY, gardening, tools)
Typical Symptoms:
Diffuse aching, stiffness, weakness, worse at the end of the day.
8. Inflammatory Conditions
Inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, gout, psoriatic arthritis, and lupus can all affect the back of the hand. These autoimmune or metabolic conditions cause the joints and soft tissues to become irritated and swollen, leading to persistent pain and stiffness.
Unlike overuse conditions, inflammatory problems often affect both hands and multiple joints at once and symptoms often appear without obvious activity triggers.
Medical conditions that often cause pain in the back of the hand include:
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Gout
- Psoriatic arthritis
- Lupus-related inflammation
Typical Symptoms:
Morning stiffness, swelling, warmth, symmetrical involvement.
Diagnosis: How Is Back of Hand Pain Identified?
When assessing back of hand pain, your physician will look at:
- Exact pain location
- Onset pattern (sudden vs gradual)
- Symptoms during movement
- Swelling, deformity, or numbness
- Grip strength and finger function
- Sensation changes
Further investigations may be necessary including:
- X-ray: to rule out fractures or arthritis
- Ultrasound: for tendon or soft tissue injuries and cysts
- MRI: if diagnosis is unclear or symptoms persist
- Nerve Testing: if numbness/tingling/weakness persists
When to See a Doctor
Get medical advice if you notice:
- Severe pain or swelling after an injury e.g. fall or direct impact
- Visible deformity
- Numbness or tingling that isn’t improving
- A lump that is growing or causing pain
- Inability to move wrist or fingers normally
- Pain lasting longer than 2–3 weeks despite rest
Treatment for Posterior Hand Pain
Treatment depends on the underlying cause, but the good news is that most cases of pain in the back of the hand settle really well with simple, conservative care. As a physio, these are the treatments I find make the biggest difference.
1. Rest & Activity
Modification
Giving the irritated tissues a break is often the quickest way to ease pain on the back of the hand.
What to do:
- Avoid or reduce repetitive gripping, lifting, pushing, or typing activities
- Break up tasks into smaller chunks to reduce strain
- Switch to lighter tools or ergonomic equipment where possible
- Avoid weight-bearing through the hand during flare-ups
If pain started suddenly during sport, manual work, or DIY, allow a short period of relative rest to calm things down.
Why it helps:
Rest reduces tendon and joint irritation, lets inflammation settle, and prevents symptoms from becoming chronic.
2. Ice or Heat
Both ice and heat can be helpful for reducing posterior hand pain. Which one to use depends on your symptoms.
Ice is best for:
- Sharp pain in the back of the hand
- Swelling
- Recent injuries or flare-ups
- Tendonitis or ligament sprains
Apply an ice pack for 10–15 minutes, 2–3x/day.
Heat is best for:
- Stiffness or tightness, especially in the morning
- Chronic aching
- Arthritis-related pain back of hand
A heat pack or warm water soak for 10 minutes works well.
3. Splints & Supports
Supporting the hand or wrist in a splint can significantly reduce dorsal hand pain by offloading irritated tissues and reducing movement-related pain and instability.

Splints may help with:
- Extensor tendonitis
- Intersection syndrome
- De Quervain’s
- Ligament sprains
- Early arthritis flare-ups
- Ganglion cysts
How they help:
Splints reduce strain on the extensor tendons and stabilise irritated joints, allowing them to settle faster.
4. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is one of the most effective treatments for back of hand pain, and it is where I see the biggest improvements with my patients.
Common physical therapy techniques that I find the most useful for reducing pain in back of hand are:
- Stretching & Strengthening Routines: tailored to the fingers, wrist, and forearm
- Tendon Gliding: to reduce irritation and improve smooth tendon movement
- Joint Mobilisation: for stiff CMC/MCP joints or wrist tightness
- Postural Correction: especially if neck or radial nerve irritation is contributing
- Ergonomic Training: for computer users, tradespeople, gym-goers, and those with repetitive strain
Exercise examples include:
- Wrist Extension Strengthening: great for tendonitis and dorsal wrist pain
- Finger Extensor Stretches: reduce tightness and improve tendon mobility
- Grip Strengthening: essential once pain starts to settle
- Nerve Glides: for radial nerve compression or Wartenberg’s Syndrome
- Stability Training: for ligament sprains or wrist instability
Physio ensures tissues heal properly and reduces the chance of recurring pain.
5. Medication
Over-the-counter medication can be helpful while symptoms settle.
Medication options include:
- NSAIDs: (ibuprofen, naproxen) if appropriate, to reduce inflammation and pain
- Topical Anti-Inflammatories: like Voltarol gel
- Paracetamol: for pain relief
6. Steroid Injections
Used sparingly, steroid injections they can be very effective in the right situation, particularly for stubborn or inflamed conditions, including:
- Painful ganglion cysts
- De Quervain’s symptoms that aren’t improving
- Arthritis flare-ups
- Persistent tendon inflammation
They provide targeted, fast-acting relief — often allowing you to progress with physio more comfortably. However, they do temporarily weaken the area so care should be taken for the first few days.
7. Surgery (rare)
Surgery is only needed when conservative treatment hasn’t worked or when there is a structural issue that simply can’t heal on its own.
Surgery may be considered for back of hand pain from:
- Persistent or recurrent ganglion cysts
- Severe arthritis that is affecting function
- Tendon ruptures
- Fractures that haven’t healed or involve joint alignment
- Significant scapholunate ligament injuries
For most people, surgery is a last resort - and thankfully, most cases of back of hand pain never reach this stage.
How to Prevent Dorsal Hand Pain
A few small habits can make a big difference and reduce your chance of developing back of hand pain:
- Use ergonomic keyboard/mouse
- Take regular breaks from gripping or typing
- Strengthen extensor tendons
- Stretch fingers and wrists daily
- Avoid gripping tools too tightly
- Manage inflammatory conditions early
- Build-up training load gradually with weights
Pain In Back Of Hand Summary
Pain in the back of the hand is a common problem that can make everyday tasks like typing, gripping, or lifting uncomfortable. It usually arises from extensor tendon irritation, joint problems (arthritis or sprains), nerve compression, ganglion cysts, or direct injuries to the bones or ligaments.
Key takeaways about pain in back of hand:
- Causes: Overuse, repetitive strain, minor injuries, inflammation, or degenerative conditions.
- Symptoms: Aching, stiffness, sharp pain in back of hand with movement, swelling, tenderness, burning, tingling, reduced grip strength, or visible lumps.
- Diagnosis: Usually clinical, sometimes confirmed with X-ray, ultrasound, or MRI if needed.
- Treatment: Most cases respond well to rest, ice or heat therapy, splints, physical therapy, ergonomic adjustments, and gradual strengthening exercises. Medications, steroid injections, or surgery are reserved for persistent or severe cases.
- Prevention: Ergonomic habits, regular hand and wrist exercises, pacing repetitive activities, and early management of inflammatory conditions help reduce risk.
Bottom line: Early recognition and treatment of dorsal hand pain are key to faster recovery and preventing chronic problems. Most people regain full hand function with conservative care, but any persistent pain, swelling, numbness, or visible lumps should be assessed by a healthcare professional to rule out more serious conditions.
Related Articles
Medical & Scientific References
- Pain In The Back Of The Hand. NHS UK
- Pain In The Back Of The Hand. Specialists in Sports and Orthopedic Rehabilitation (SSOR)
- The prognosis of pain and function in people with hand and thumb base osteoarthritis: a systematic review. Annals Of Medicine
- Reduced pain and improved daily activities for individuals with hand osteoarthritis using a silicone wrist hand orthosis. Journal Of Hand Therapy
Page Last Updated: January 2nd, 2026
Next Review Due: January 2nd, 2028